The 5 C’s of Diamond Certification
The 5 C’s in the diamond grading process relate to Carat, Cut, Colour, Clarity and Certification. In this educational blog article we discuss these diamond characteristics.
The characteristics of a diamond is usually determined by having the diamond sent to a gemmological laboratory for independent grading. The quality and integrity of these diamond laboratories is therefore very important as if the grading is incorrect you might be buying a poor quality diamond but paying for a high quality premium diamond. The Gemmological Institute of America (GIA) is regarded around the world as the leading authority on all things diamond and gemmological. As industry guardians and inventors of the modern grading system we sell and recommend that all diamonds are graded by the GIA. If a diamond is graded by a lesser authority than the GIA the carat, cut, colour or clarity can be over stated resulting in consumers buying a diamond that is incorrect (a lemon). Polished Diamonds sell GIA certified diamonds for your assurance and safety. Review the educational diamond information below and contact us to speak with our certified diamond grader if you have any questions - we like to chat and help.
1. Diamond Carat
Carat is a measurement of weight as opposed to size. Originally a ‘carab’ was a seed which was used as a weight measure and this is where the word carat originally derived its name. 1 carat is equal to 100 points; so 75 points is 75% of a carat or 0.75 carat. Carat is the most price sensitive part of a diamond as it technically refers both to the mass and a proportionate size. Diamonds are an extremely rare stone and as the size and carat weight increase they become even harder to source. The ever decreasing supply of high carat diamonds tempered with an ever increasing demand for them continues to push the price equilibrium upwards.
Half carat diamonds (0.50ct) are very popular as you get an excellent value to weight ratio. Once a diamond hits 1 carat, the price increases exponentially to the final size. For example a 0.50ct round diamond measures about 5.00mm across the face. If we increase and double the weight to 1.00ct the size increases to about 6.30mm. This example shows that if we double the carat weight we only increase the size by 20% and yet the price will increase by around 3 times.
We think the ‘sweet spot’ for an average income is somewhere between 0.50ct to 0.70ct. Increasing the size will increase the value to price ratio. Most women prefer a decent sized gem so balancing that to your budget means taking the carat weight into account and also considering the other main considerations of colour, clarity, cut and ultimately certification.

2. Diamond Clarity
Clarity refers to the transparency within and around the diamond. Diamonds have imperfections both internally and externally that are called inclusions. There are many different types of inclusions which are known as crystals, feathers, pin points, twinning wisps, clouds and indented naturals.
The presence of these tiny imperfections has been classified by the GIA into these specific categories:
• Internally Flawless (IF)
• Very Very Small 1-2 (VVS1, VVS2)
• Very Small 1-2 (VS1, VS2)
• Small Inclusion 1-2 (Si1, Si2)
• Lower quality, Inclusion 1-2-3 (I1, I2, I3).
The premium clarity is IF as there are no visible inclusions reported under 10 x magnification from the top down. The lowest grade is I3 where the inclusions are clearly visible and often breach the surface of the diamond. Polished Diamonds sell down to and including I1 clarity and only eye clean diamonds. Some inclusions in the I1 clarity can be visible so we take care to select inclusion characteristics like feathers, twinning twisps, indented naturals and pin points as these I1 inclusions are eye clean and represent excellent value.
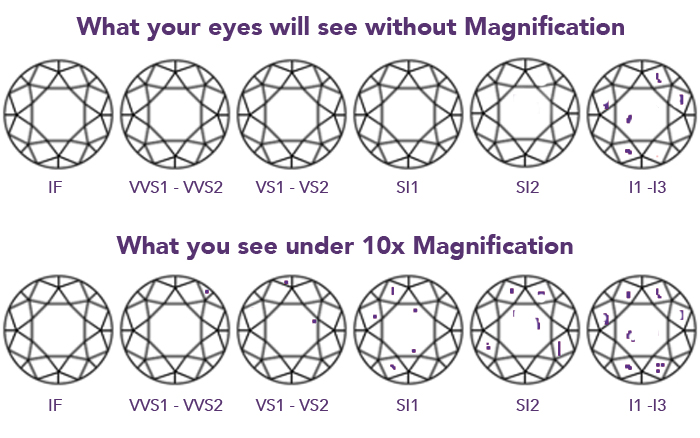
So lets look at each clarity level in more detail:
Internally Flawless (IF)
IF clarity is internally flawless and the best level of clarity that money can buy. These sought after diamonds are extremely rare and are priced accordingly. The IF diamond is loupe clean at 10 x magnification and is perfectly eye clean.
Very Very Small 1-2 (VVS1, VVS2)
VVS1 – VVS2 clarity is Very Very Small (VVS) and often this means there will be a single inclusion that is so minimal that it is virtually impossible to see with the naked eye and even very difficult to detect at 10 x magnification. The VVS clarity grade is priced accordingly yet is very rare also. We often urge clients to consider buying an IF (Internally Flawless) diamond as VVS is so close in both clarity and price that often it is worth paying the small difference to have the satisfaction of having the best that money can buy. VVS1 and VVS2 is a high grade diamond and is also eye clean.
Very Small 1-2 (VS1, VS2)
VS1 – VS2 clarity diamonds have Very Small (VS) inclusions and we recommend this level if you want a higher clarity level than most High Street stores generally provide and yet they remain well within most budgets. The VS clarity range is also100% eye clean and even difficult to detect under 10 x magnification. VS clarity is a very high quality benchmark in diamonds and still remains a clear statement of quality.
Small Inclusion 1-2 (Si1, Si2)
Si1 – Si2 clarity diamonds have Small Inclusions (Si) which are also eye clean yet are easily detected under 10 x magnification. These diamonds provide extremely good value to our clients as it enables you to increase your carat/colour/cut comparatively to your budget. We recommend an Si1 over an Si2 to ensure that the inclusion is small enough to remain invisible to the naked eye. An Si2 clarity may still be considered but some people with excellent eyesight, under correct lighting and who can train their eye on a certain point may detect the imperfection of an Si2 by the naked eye. Therefore we generally recommend an Si1 clarity grading.
Lower quality, Inclusion 1-2-3 (I1, I2, I3)
Polished Diamonds does provide I1 clarity diamonds by request as they can be eye clean. The trick is to avoid black crystal inclusions which can be more easily seen than white inclusions that hide in the facets. Diamonds that are I1 clarity and eye clean represent very good value if size matters and price is sensitive. We do not sell I2-I3 clarity range as we feel that this quality level is not good enough for our clients as the marks can be seen and these are best suited to the mass produced chain stores. The clarity of I2-I3 are typically not eye clean and as anyone can easily see the imperfections on the diamond with the naked eye this devalues the quality you’d expect from professional Jewellers. These imperfections can include surface breaching and internal fractures which not only look second rate but also compromise the long term strength of the diamond. Many retail Jewellery chains offer these low clarity I2-I3 diamonds as they are inexpensive resulting in higher profits but unhappy clients.
Above is a simple graphic to help show the clarity levels and the inclusions involved. It is important to remember that IF-VVS1-VVS2-VS1-VS2-Si1-Si2 and I1 diamonds are eye clean meaning you will not see any visual imperfections. On this basis we recommend Si1, Si2 and I1 as an economical clarity, VS as high quality option and then jump to IF if you want your diamond to be perfectly flawless! Avoid I2-I3 clarity as these diamonds are heavily marked.
We love to help.
If you want to know more about diamond clarity be sure to click the live chat, email or call us to discuss it further. Diamond clarity is a large subject and we can inform you quickly with correct information.
3. Diamond Cuts
The cut is used to describe the shape, the make or angles of a diamond. When describing the diamond shape we call this the cut macro and when describing the intricate angles, facets and measurements of a diamond we call this the cut micro.
So first let’s discuss the diamond cut macro or shapes.
Diamond Shapes
Diamonds are cut to retain weight and yield from the rough crystal. When diamonds are mined they appear in shapes such as dodecahedron, octahedron, flats, macles and others. The diamontaire examines the rough diamond to decide what shape will maximise his profits and this is usually driven by the weight or carat.
The shapes available to the diamond cutter are almost endless but the main shapes include:
• Round Square (Princess)
• Radiant
• Emerald
• Asscher
• Pear
• Marquise
• Cushion
• Oval
• Heart

The GIA utilise technical names for these polished diamond shapes for example a Princess cut diamond is called a “square modified brilliant” and a Radiant cut diamond is called a “cut cornered rectangular modified brilliant”.
The most popular diamond shape is the Round Brilliant closely followed by a Princess or square diamond. We think all diamond shapes are fantastic so please explore our extensive diamond database to select a diamond that specifically appeals - call for a chat, live chat or email - we like to help and can give you correct information to assist with your purchase.
Diamond Cut - Micro:
The internet has radically improved access to information regarding the various qualities of cut diamonds and this transformed the diamond industry during the 90’s forcing it to focus more directly on diamond cut in a micro sense which means making a diamond perform better by shaping it to primarily optimise light refraction and therefore generate a lot more sparkle.
The GIA instigated a cut grade system after 15 years of research in 2006 and this system is the most complete and accurate grading system to date. It relies on a practical, comprehensive scientific approach that protects consumers so that diamond cutters can achieve a desired cut and increase the performance and light return of a diamond.
The GIA diamond cut grade system includes the grades : Poor, Fair, Good, Very Good and Excellent. Estimating a cut grade is a very complex task that includes measuring the micro angles, facets, %percentage relationships and the all round shapes within the diamond. These measurements include the pavilion, table, girdle, culet, keel, crown and the facet work. The relationships between these parts of the diamond are very important and laser light tracing equipment is utilised to calibrate and measure it accurately.
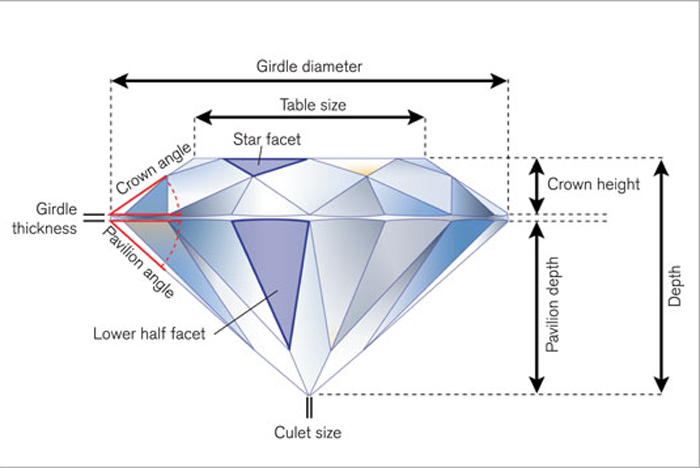
When buying a GIA certified diamond you can be assured that all the hard work has already been done for you. Many years of intense analysis and study have gone into calculating these cut grade qualities and these internationally respected gradings can be trusted implicitly.
At Polished Diamonds we sell Very Good and Excellent cut diamonds as they are high performing and return more light and sparkle. The differences between a Very Good cut and an Excellent cut is barely noticeable yet the difference between a Good to a Very Good is more obvious. We recommend a Very Good or Excellent cut grade for a maximum sparkle, enjoyment and future happiness.
4. Diamond Colour
Diamonds come in many different colours but the majority of high quality diamonds are found within the white spectrum. The Gemmological institute of America (GIA) invented the current diamond grading system and assigned specific letters to describe a diamond’s colour at a glance.
The best colourless diamond is know as a D and the most yellow saturated diamond in the white spectrum is a Z; so the colour spectrum is alpha based from D-Z. At Polished Diamonds we sell only high quality diamonds so we have committed to selling diamonds that are certified between D-J. The higher the colour the more rare it is and higher the price. A colourless diamond also reflects sparkle and return better simply because the colour saturation does not cloud the light refraction.
Lets look at Diamond colour in more detail:
D-F Colour Grade
Colourless Diamonds include the range from D-E-F. These diamonds do not show any yellow hue whatsoever. Diamonds of D-E-F colour are excellent for Platinum, White Gold and Palladium diamond rings but they do cost more.
G-H Colour Grade
Diamonds in the range G-H are nearly colourless and offer extremely good value. Buying a G-H colour diamond will enable the carat weight of the diamond to be increased for the same price as they are not as expensive as the D-E-F range. There is no obvious yellow hue in G-H colour diamonds which makes them excellent value and a good economical choice for Platinum, White Gold and Palladium settings and a top selection for Yellow Gold. The G-H colour diamonds are excellent for yellow gold jewellery because there is sufficient yellow reflection from the gold to warrant not using a D-E-F colourless diamond.
I-J Colour Grade
The diamond colours of I-J are still near colourless and are best suited if carat weight and size is important. The I-J colour diamonds are also excellent especially if yellow gold is being used as a base metal for your jewellery.

Be sure to ask if you have any questions regarding these technical aspects of GIA certification. Our qualified staff would be more than happy to help. Below is an educational video from the GIA you might like to watch:



FaceBook Twitter YouTube Google Instagram pinterest